

In chemistry there are millions of chemical reactions. But most reactions can be classified as one of four types of reactions:
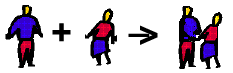
In the simplest type of synthesis reaction, two elements combine to form a compound. When writing these be sure to include a subscript 2 under any diatomic elements (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine).
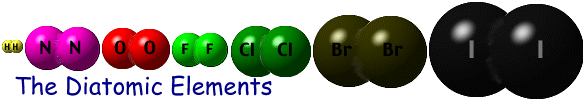
And sometimes two compounds can combine to form an even bigger compound.
In our dancers analogy, boy A steps on girl B's toe. She gets upset and walks away.
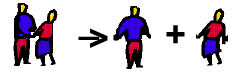
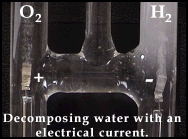
In our dance analogy, Boy A and Girl B are dancing. In walks boy C, who happens to wish to dance with Girl B. If he is strong enough he can push out Boy A and dance with girl B. Now boy A is by himself. In this analogy the boys are metals and the girl is the nonmetal.
What do you think
would had happened if Boy C wasn't strong enough to push out Boy
A? You go it - nothing would have happened. Same goes with a
single replacement reaction. If the element is not more chemically
active than the element (in the compound) it is trying to replace,
no reaciton will occur.
Generally, as you go across the periodic table (from I-A to
IIIV-A) metals become less chemically active. A metal such as
magnesium is more chemically active that transition metals such as
copper, tin or zinc. An easier way to identify the activity of
element is to use an activity series which shows the chemical
activity of both metals and nonmetals.
|
|
Metals Nonmetals lithium fluorine potassium chlorine calcium bromine sodium iodine magnesium oxygen aluminum nitrogen zinc chromium iron nickel tin lead hydrogen* copper mercury silver platinum gold |
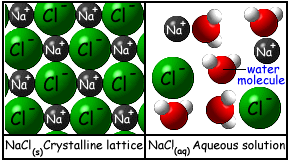
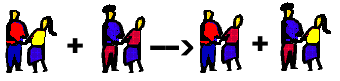
To use our analogy of dancers: Two couples are dancing . The two girls look over and state they wish to switch partners. And so...they do.
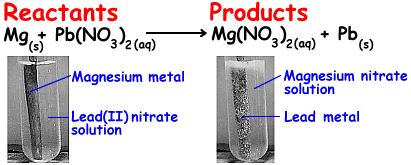
For a double replacement reaction to occur, one of the products must be insoluble and form a solid. This solid, called a precipitate, is more dense than the surrounding solution and falls to the bottom of the test tube. An arrow down is used to identify a precipitate. If both products are soluble (remain dissolved) then there is no reaction.
|
Anion |
Solubility |
|
nitrates |
all soluble |
|
nitrites |
all soluble except with Ag+ |
|
chlorides |
all soluble except with Ag+, Hg+, Pb+2, Cu+ |
|
bromides |
all soluble except with Ag+, Hg+, Pb+2, |
|
iodides |
all soluble except with Ag+, Hg+, Pb+2, |
|
sulfates |
all soluble except with Ag+, Ba+2, Sr+2, Ca+2 |
|
sulfites |
all INSOLUBLE except with any alkali metal, NH4+ |
|
sulfides |
all INSOLUBLE except with any alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, NH4+ |
|
phosphates |
all INSOLUBLE except with any alkali metal, NH4+ |
|
carbonates |
all INSOLUBLE except with any alkali metal, NH4+ |
|
oxides |
all INSOLUBLE except with any alkali metal, alkaline earth metal |
|
hydroxides |
all INSOLUBLE except with any alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, NH4+ |

BaBr2(aq) + KI(aq) --> No Reaction (both the products BaI2 + KBr are soluble in water and do not form a precipitate.)
MgSO4 + Fe(NO3)2 --> No Reaction (both the products Mg(NO3)2 + FeSO4 are soluble in water and do not form a precipitate.)
